Configure risk-based adaptive authentication¶
This guide shows you how to use ELK Analytics to assess an end user's risk score and enable adaptive authentication.
Scenario¶
Consider a business use case where a bank wants to prompt an additional authentication step when a user attempts to log in to the system after making transactions amounting to over $10,000 within five minutes.
The diagram below shows how the connection between the client applications, ELK Analytics, and MWARE IAM works to assess the risk of the user.
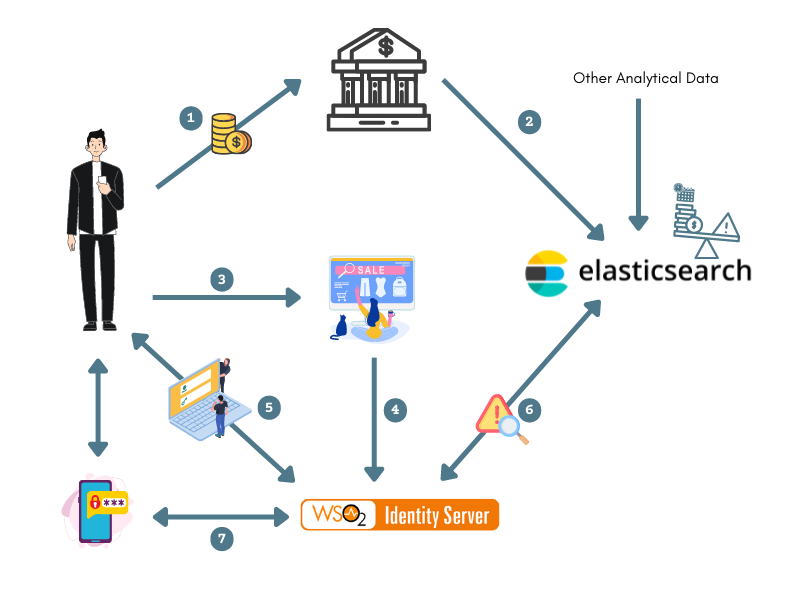
- The user performs bank transactions through different applications.
- Transaction data from all these applications are published to the ELK Analytics via the “transaction” index.
- The user attempts to access an application that uses MWARE IAM as the identity provider.
- The application sends an authentication request to MWARE IAM.
- The user is prompted to log in, and MWARE IAM authenticates the user using basic authentication (username/password credentials).
-
MWARE IAM publishes an event to ELK, which computes the user's risk score based on the user's transaction history using the data received in step 2.
For example
If the user has made transactions that add up to over $10,000 within the last five minutes, the risk score is 1. Else, the risk score is 0.
-
If the risk score is 1, MWARE IAM prompts an additional step of authentication for the user (i.e., entering a hardware key number) before allowing the user to access the service provider application.
Prerequisites¶
- See the general prerequisites for all adaptive authenticaiton scenarios.
- You need to set up the sample application.
-
You need to configure ELK analytics for adaptive authentication, and run the following command to create an index named
transactionto store transaction data.Info
Replace
{ELASTICSEARCH_HOST}and{ELASTICSEARCH_BASIC_AUTH_HEADER}to match your settings.Request Format
Sample Requestcurl -L -X PUT 'https://{ELASTICSEARCH_HOST}/transaction' -H 'Authorization: Basic {ELASTICSEARCH_BASIC_AUTH_HEADER}' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{"mappings":{"properties":{"@timestamp":{"type":"date"}}}}'
Responsecurl -L -X PUT 'https://localhost:9200/transaction' -H 'Authorization: Basic d3NvMnVzZXI6Y2hhbmdlbWU=' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{"mappings":{"properties":{"@timestamp":{"type":"date"}}}}'{ "acknowledged": true, "shards_acknowledged": true, "index": "transaction" }
Configure risk-based authentication¶
To configure risk-based authentication:
-
On the management console, go to Main > Identity > Service Providers > List.
-
Click Edit on the
saml2-web-app-pickup-dispatch.comservice provider. -
Expand the Local and Outbound Authentication Configuration section and click Advanced Configuration.
-
You will be redirected to Advanced Configuration, expand Script Based Conditional Authentication.
-
In the Templates section, click on the
+corresponding to the ELK-Risk-Based template.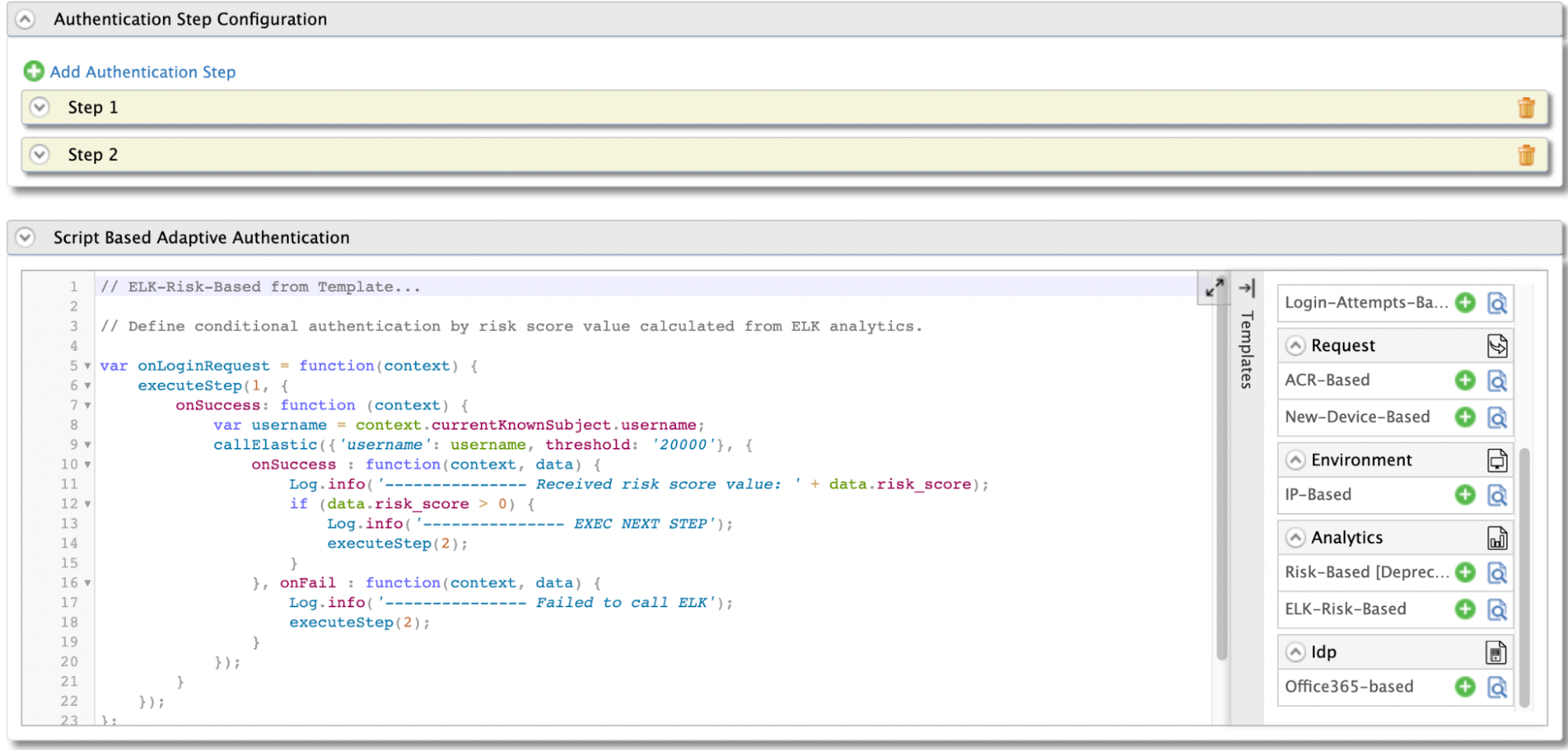
-
Click Ok to add the authentication script. The authentication script and authentication steps will be configured.
Info
- The resulting authentication script defines a conditional step that executes the second authentication step if the
riskScoreis greater than 0. - By default,
TOTPwill be added as the second authentication step. You can update this with any authentication method.
- The resulting authentication script defines a conditional step that executes the second authentication step if the
-
Click Update to save your configurations and restart MWARE IAM.
Try it out¶
-
Start the Tomcat server and access the following sample PickUp application URL:
http://localhost.com:8080/saml2-web-app-pickup-dispatch.com. -
Log in to the application by giving your username and password.
Note
The user is authenticated with basic authentication only.
-
Log out of the application, and execute the following cURL command. This command publishes an event regarding a user bank transaction exceeding $10,000.
Request
Sample Requestcurl -L -X POST 'https://{ELASTICSEARCH_HOST}/transaction/_doc' -H 'Authorization: Basic {ELASTICSEARCH_BASIC_AUTH_HEADER}' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{ "@timestamp":"{CURRENT_TIMESTAMP}", "username":"{USERNAME}", "amount": {TRANSACTION_AMOUNT} }'
Responsecurl -L -X POST 'https://localhost:9200/transaction/_doc' -H 'Authorization: Basic d3NvMnVzZXI6Y2hhbmdlbWU=' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{ "@timestamp":"{{currenttimestamp}}", "username":"Alex", "amount": 12000 }'{ "_index": "transaction", "_id": "_75YR4EBPqDnJYiU7W_A", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 0, "_primary_term": 1 } -
Log in to the application again. You are now prompted for the
TOTPafter the basic authentication.Info
Before executing the cURL command given in step 4, the user had no transaction history, and the user's riskScore was 0. The authentication script is programmed to prompt only basic authentication if the risk score is 0.
After executing the command, a transaction event that indicates the user spending more than $10,000 is published and recorded in the Siddhi application. Therefore, when the user attempts to log in again, the user's riskScore is evaluated to 1, and the user is prompted for an extra authentication step.