User Management Architecture¶
User management functionality is provided by default in MWARE IAM. The following documentation introduces the main concepts in User Management, such as users, roles, permissions, user stores etc. and how they are used in MWARE IAM.
User management involves defining and managing users, roles, and their access levels in a system. A user management dashboard or console provides system administrators with a high-level view of a system's active user sessions, their log-in statuses, the privileges of each user, and their activity in the system, enabling system admins to make business-critical, real-time security decisions. A typical user management implementation involves a wide range of functionality such as adding/deleting users, controlling user activity through permissions, managing user roles, defining authentication policies, managing external userstores, manual/automatic log-out, and resetting user passwords.
Any user management system has the following basic components:
- Users: Users are consumers who interact with your organizational applications, databases, and other systems. A user can be a person, a device, or another application/program within or outside of the organization's network. Because users interact with internal systems and access data, security-conscious organizations need to define which data and functionality each user can access by assigning permissions.
- Permissions: A permission is a delegation of authority or a right that is assigned to a user or a group of users to perform an action on a system. Permissions can be granted to or revoked from a user, user group, or user role automatically or by a system administrator. For example, if a user has the permission to log in to a system, the permission to log out is automatically granted as well.
- User roles: A user role is a grouping of permissions. In addition to assigning individual permissions to users, admins can create user roles and assign those roles to users. For example, you might create user roles called VP, Manager, and Employee, each of which has a different set of permissions, and then assign those roles to users based on their position in the company. Then, if you need to modify the permissions of all your managers, you can simply modify the Manager user role, and all users with that role will have their permissions updated automatically.
The following diagram illustrates how the user management functionality is structured to work in MWARE IAM:
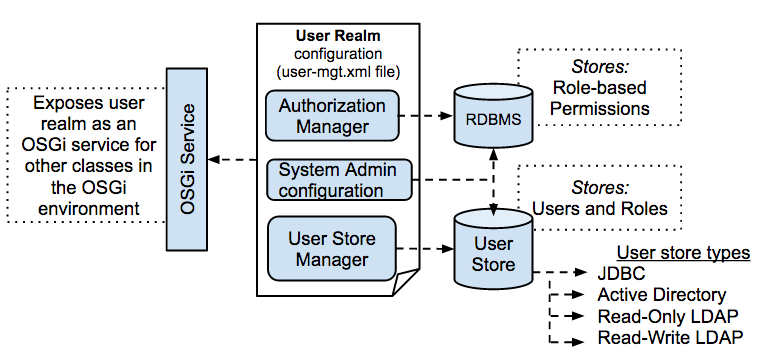
- Userstores: A userstore is the database where information about the users and user roles is stored, including log-in name, password, first name, last name, and e-mail address.
- RDBMS (for Authentication and Authorization): This RDBMS stores information of the role-based permissions.
Info
According to the default configuration in MWARE IAM, the embedded H2 RDBMS that is shipped with the product is used as the userstore as well as the RDBMS for storing information related to permissions.
-
Realm configuration: The user realm consists of the configurations required to initialise the user realm. This includes setting up the userstore Manager, the Authorization Manager and the System Administrator. These configurations are explained below.
Userstore Manager The Userstore Manager is responsible for managing the underlying userstore. It is represented by the
UserStoreManagerJava interface. There can be different userstore Manager implementations to connect with different userstores, but you can configure only one Userstore Manager implementation in a single user realm (that is, a single WSO2 Carbon instance). The userstore Manager can be operated in both read/write mode and read-only mode. In read-only mode, you can only connect with an existing userstore. MWARE IAM provides the following default Userstore Manager implementations:JDBCUserStoreManager(read and write)LDAPUserStoreManager(read-only)ApacheDSUserStoreManager(read and write)
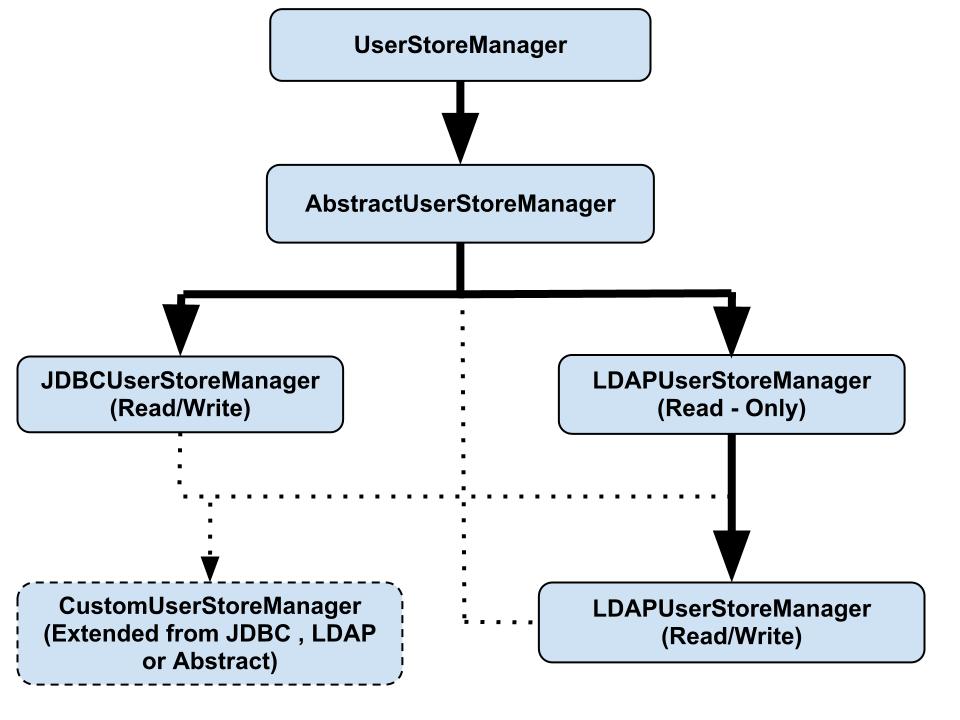
You can write a custom userstore manager implementation by implementing
UserStoreManageror by extendingAbstractUserStoreManageror one of the default implementations.Using JDBCUserStoreManager
The
JDBCUserStoreManagerclass uses a schema that is specific to WSO2 Carbon. It contains the following tables:- UM_USER: Contains user names and passwords
- UM_ROLE: Contains role names
- UM_USER_ROLE: Contains user role mappings
- UM_USER_ATTRIBUTE: Contains user attributes. There can be any attribute ID and a value for that attribute ID that is associated with a user’s profile.
You can find the full schema of these tables from the database script files in the
<IS_HOME>/dbscriptsdirectory. Note that these scripts also contain schemas for other tables that are used for user management and registry functions. If your organization contains an existing JDBC userstore that you want to use with a MWARE IAM, you must extendJDBCUserStoreManagerand write a new implementation for your userstore according to your schema.Authorization Manager The Authorization Manager uses role-based access control (RBAC) to protect resources related to the WSO2 Carbon platform. The default implementation of the Authorization Manager is JDBCAuthorizationManager, which uses a permission model specific to WSO2 Carbon and uses the authorization data that is stored in tables in the JDBC database. You can replace this implementation with a custom implementation (for example, if you want to use a XACML authorization manager) and use it with MWARE IAM.System Administrator The system admin user is typically the super tenant user, who by default has permission to perform all administration tasks in the server. The admin user will thereby create other tenant users and define roles with permissions. Once this is done, the other tenant users will be able to log in to their respective tenant domains and use the server according to the permissions that have been granted. Note that the permissions granted to the Super Tenant user cannot be modified.