Introduction to Authentication¶
User identity¶
The way in which a user can be uniquely identified is called user identity. A user’s identity can differ based on the platform and the use case. Considering the digital world a single user can have different identifying attributes such as user name, user ID, biometric information, etc.
Authentication¶
Simply, Authentication is validating the user’s identity. During the user onboarding process, the user’s identity is shared and stored with the system. When a user needs to access the system later, the system checks and verifies whether it is really the particular user who is trying to access the system by using that shared identity. Several factors for authentication can be applied based on the security level of the server or based on what the system needs to achieve.
There are three types of authentication.
- Single-factor authentication
- Two-factor authentication
- Multi-factor authentication
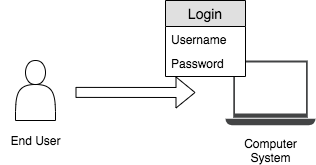
Single-factor authentication¶
This is a process for securing access to a given system to identify the party requesting access through only one category of credentials. Any type of credential can be used for this even though the most typical and popular example of this is a password (credential) to a username. As this approach requires a single credential, if that credential is exposed to the public, anybody can access the system. Therefore, considering the other two authentication mechanisms, this method is less secure.
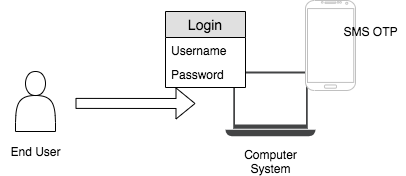
Two-factor authentication¶
This authentication requires a two-step verification process. Therefore, the party requesting the access should use two credentials. These credentials can be something the user knows (answer to a challenge question), something the user owns (SMS OTP), etc. This method is stronger than single-factor authentication but weaker than multi-factor authentication.
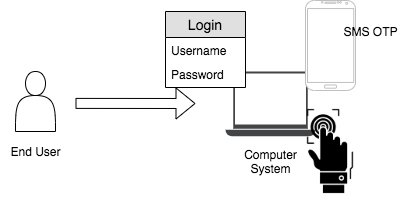
Multi-factor authentication¶
This method utilizes factors that are independent of each other such as something you know, something you have, and something you are, in order to eliminate any data exposure. For example, a system that is secured using multi-factor authentication (MFA) can use three verification steps such as username-password credentials, SMS OTP, and fingerprint to authenticate a user to the system.